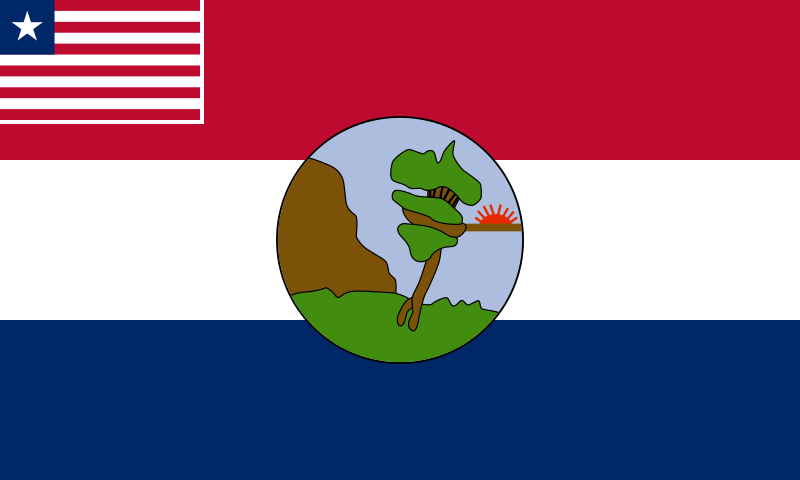
LIBERIA
The flag of Liberia, sometimes called the Lone Star (not to be confused with "The Lone Star State", a nickname for Texas), bears a close resemblance to the flag of the United States, representing Liberia's founding by former black slaves from the United States and the Caribbean. They are both part of the stars and stripes flag family. The Liberian flag has similar red and white stripes, as well as a blue square with a white star in the canton. It was adopted on 24 August 1847.
Motto: "The Love of Liberty Brought Us Here"
The National Anthem of Liberia
The Country name derives from the Latin word "liber" meaning "free"; so named because the nation was created as a homeland for liberated African-American slaves.
Capital:
Monrovia
Capital Geographic Coordinate:
6 18 N, 10 48 W
Country Name:
Liberia
Country Full Name:
Republic of Liberia
Calling Code: +231
Internet TLD: .lr
Official Languages: +231
ISO 3166 Code: LR
Independence:
26 July 1847
Country Full Name:
Republic of Liberia
Total Area:
43,000 Square Miles; 111,369 Square Kilometers
Border Countries:
It is bordered by Sierra Leone 306 km to its northwest, Guinea 563 km to its north, Ivory Coast 716 km to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean to its south and southwest with 360 Miles or 579 Kilometers of coastline.
Currency:
Liberian Dollar (LRD)
GDP - per capita (PPP):
$900.00 (USD)
Capital Time Difference
UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
Location:
Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Cote d'Ivoire and Sierra Leone
Population:
5,073,296
Population Growth Rate:
2.56%
Exports:
$1,197,000,000 USD (Major Exports rubber, timber, iron, diamonds, cocoa, coffee)
Imports:
$7,143,000,000 USD (Major Imports fuels, chemicals, machinery, transportation equipment, manufactured goods; foodstuffs
FACTS
-
Liberia has an economy that is primarily based on agriculture, mining, and forestry. Here are key points about Liberia's economy:
1. Agriculture:
- Agriculture is a significant sector, employing a large portion of the population. Key crops include rubber, palm oil, cocoa, coffee, and rice.
- Subsistence farming is common, with rice and cassava being major food staples.
2. Mining:
- Liberia is rich in natural resources, particularly iron ore, gold, and diamonds.
- The mining sector has attracted significant foreign investment, although it has faced challenges such as fluctuating global commodity prices and political instability.
3. Forestry:
- Timber is another important natural resource. The country has extensive tropical rainforests, and logging has historically been a key economic activity.
- Efforts to manage forests sustainably have increased, especially after periods of illegal logging during the civil wars.
4. Economic Growth and Challenges:
- The economy experienced significant disruption due to two civil wars (1989-1996 and 1999-2003), which damaged infrastructure and decreased economic output.
- Since the end of the civil wars, Liberia has made strides in rebuilding its economy, although it continues to face challenges such as poverty, unemployment, and limited access to education and healthcare.
5. Foreign Aid and Investment:
- International aid has played a critical role in Liberia’s post-war recovery, with major contributions from the United States, the European Union, and other international organizations.
- Foreign direct investment, particularly in mining and agriculture, has also been crucial for economic growth.
6. Infrastructure and Development:
- Infrastructure remains underdeveloped, with poor road networks, limited electricity supply, and inadequate healthcare facilities.
- The government and international partners are working on various projects to improve infrastructure, including road rehabilitation and expansion of the electricity grid.
7. Monetary Policy and Banking:
- The Central Bank of Liberia regulates the financial sector, which includes commercial banks and microfinance institutions.
- The Liberian dollar is the national currency, but the US dollar is also widely used.
8. Economic Diversification:
- Efforts are being made to diversify the economy beyond traditional sectors. This includes developing the tourism sector and encouraging small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Despite these efforts, Liberia’s economy remains vulnerable to external shocks, such as commodity price fluctuations and global economic downturns. The country's long-term economic growth depends on continued political stability, effective governance, and sustained investment in infrastructure and human capital.
-
Population
Liberia has a population of around 5 million people. The population is young, with a significant proportion under the age of 15.
Ethnic Groups
Liberia is ethnically diverse with over 16 major ethnic groups, including:
- Kpelle (the largest group), Bassa, Gio (Dan), Kru, Grebo, Mano, Mandingo, Krahn, Vai, Gola, Gbandi, Loma, Kissi, Dei, Belle, Mende
Language
English is the official language of Liberia. However, numerous indigenous languages are spoken, reflecting the country's ethnic diversity. Some of the widely spoken indigenous languages include Kpelle, Bassa, Kru, and Grebo.
Religion
Liberia is predominantly Christian, with about 85% of the population adhering to various Christian denominations. Islam is practiced by about 12% of the population, mainly among the Mandingo and Vai ethnic groups. A small percentage of the population adheres to indigenous religious practices or other faiths.
Urbanization
Monrovia, the capital city, is the largest urban center in Liberia and home to a significant portion of the population. Other major cities include Gbarnga, Buchanan, and Kakata. Urban areas are characterized by a higher population density compared to rural areas.
Health and Education
The country faces challenges in health and education, with limited access to healthcare facilities and schools in many regions. Efforts are ongoing to improve these sectors, but infrastructure and resource constraints remain significant hurdles.
Migration and Diaspora
Liberia has a history of migration due to civil conflicts and economic opportunities. Many Liberians live abroad, particularly in the United States, which hosts a large Liberian diaspora community.
Economy and Employment
The economy of Liberia is primarily based on agriculture, mining, and forestry. Unemployment and underemployment are high, especially among the youth, leading to significant economic challenges.
Gender
Gender disparities exist in Liberia, with women often having less access to education and economic opportunities compared to men. However, there are ongoing efforts to address these disparities and promote gender equality.
These demographics paint a picture of a diverse and vibrant society facing various developmental challenges and opportunities.
-
Traditional and Indigenous Culture
Liberian culture is rich and diverse, deeply influenced by the various ethnic groups within the country. Each group has its own distinct traditions, languages, and customs, contributing to a vibrant cultural mosaic. Traditional music, dance, and storytelling are integral aspects of daily life and communal events.
Language and Communication
English is the official language of Liberia, used in government, education, and the media. However, numerous indigenous languages are spoken, and these languages play a crucial role in cultural identity and community life. Pidgin English, known locally as "Liberian English," is widely spoken and understood.
Music and Dance
Music and dance are central to Liberian culture. Traditional music often features drums, wooden xylophones, and string instruments. Songs and dances accompany various ceremonies, including weddings, funerals, and harvest festivals. Modern Liberian music incorporates genres like gospel, hip-hop, and reggae.
Art and Craft
Liberian art includes a variety of crafts such as mask-making, weaving, pottery, and sculpture. Traditional masks are especially ft
Liberian art includes a variety of crafts such as mask-making, weaving, pottery, and sculpture. Traditional masks are especially significant, used in rituals and ceremonies to represent spirits and ancestors. Handwoven textiles and intricate beadwork are also prominent in Liberian craftsmanship.
Festivals and Celebrations
Liberia hosts numerous festivals and celebrations, many of which are rooted in ethnic traditions. Independence Day on July 26th is a major national holiday, celebrated with parades, music, and communal feasts. Ethnic groups also observe their own unique festivals, celebrating harvests, initiations, and other cultural milestones.
Food and Cuisine
Liberian cuisine is hearty and diverse, featuring ingredients such as rice, cassava, plantains, and a variety of vegetables. Popular dishes include jollof rice, palm butter, fufu, and pepper soup. Seafood is abundant, given Liberia's coastal geography, and is a staple in many meals.
Religion and Spirituality
Christianity is the predominant religion in Liberia, followed by Islam and indigenous beliefs. Religious practices and spiritual beliefs often blend traditional and modern elements, reflecting the country's diverse heritage. Churches and mosques are central to community life, providing not only spiritual guidance but also social support.
Clothing and Fashion
Traditional Liberian clothing is colorful and varied, often made from locally woven fabrics. Styles and patterns can denote ethnic identity, social status, and occasions. In urban areas, Western-style clothing is also common, especially among the youth.
Literature and Oral Tradition
Liberia has a strong oral tradition, with storytelling playing a key role in preserving history and teaching moral lessons. Folktales, myths, and proverbs are passed down through generations. Written literature, including poetry, novels, and plays, has also developed, with authors exploring themes of identity, history, and social issues.
Social Structure and Family Life
Liberian society places a strong emphasis on family and community. Extended families often live together, and social responsibilities are shared. Respect for elders is a fundamental value, and communal decision-making is common, particularly in rural areas.
Liberian culture is a blend of traditional practices and modern influences, shaped by its history, ethnic diversity, and resilience. This rich cultural tapestry is a source of pride and identity for Liberians both at home and in the diaspora.
-
Location and Size
Liberia is situated on the west coast of Africa, bordered by Sierra Leone to the northwest, Guinea to the north, Côte d'Ivoire to the east, and the Atlantic Ocean to the southwest. It covers an area of approximately 111,369 square kilometers (43,000 square miles).
Topography
The terrain of Liberia is characterized by a mix of coastal plains, rolling plateaus, and low mountains. The coastal plain extends inland for about 40 kilometers (25 miles) and is followed by rolling hills and plateaus. The northern and northeastern regions are more mountainous, with the highest point being Mount Wuteve in the Wologizi range, which rises to about 1,440 meters (4,724 feet).
Rivers and Water Bodies
Liberia has a network of rivers that play a crucial role in its ecosystem and economy. Major rivers include the St. Paul River, the St. John River, the Cestos River, and the Cavalla River, which forms part of the border with Côte d'Ivoire. These rivers provide water for agriculture, transportation, and hydropower.
Climate
Liberia has a tropical climate with distinct wet and dry seasons. The wet season typically lasts from May to October, characterized by heavy rainfall, high humidity, and thunderstorms. The dry season runs from November to April, with lower humidity and occasional harmattan winds blowing from the Sahara Desert, bringing dust and cooler temperatures.
Vegetation and Wildlife
Liberia is rich in biodiversity, with extensive rainforests covering a significant portion of the country. These forests are home to a variety of plant and animal species, including rare and endangered ones. Key wildlife includes pygmy hippos, forest elephants, chimpanzees, and various species of birds and reptiles. Protected areas like Sapo National Park are vital for conservation efforts.
Coastal Features
The coastline of Liberia stretches for about 560 kilometers (350 miles) and features sandy beaches, mangrove swamps, and lagoons. The coastal region is dotted with small fishing villages and the major port city of Monrovia, which is the capital and largest city. The coastline is also prone to erosion and rising sea levels, posing environmental challenges.
Natural Resources
Liberia is endowed with abundant natural resources, including timber, iron ore, diamonds, gold, and rubber. These resources are crucial to the country's economy, although their exploitation has also led to environmental degradation and social issues.
Environmental Challenges
Liberia faces several environmental challenges, including deforestation, soil erosion, loss of biodiversity, and pollution. Efforts are underway to promote sustainable practices and environmental conservation to mitigate these issues.
Agriculture and Land Use
Agriculture is a major part of Liberia's economy, with significant land dedicated to farming. Key agricultural products include rubber, coffee, cocoa, rice, and cassava. Shifting cultivation and subsistence farming are common practices in rural areas.
Urbanization
While the majority of Liberians live in rural areas, urbanization is increasing, particularly in and around Monrovia. Urban areas face challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, housing shortages, and waste management issues.
Liberia's geography, characterized by its diverse landscapes, rich natural resources, and tropical climate, plays a significant role in shaping the nation's economy, lifestyle, and environmental conditions.
-
Government Structure
Liberia is a republic with a representative democratic system. The government is based on the principles of separation of powers among the three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial.
Executive Branch
The President of Liberia serves as both the head of state and the head of government. The president is elected by popular vote for a six-year term and can be re-elected for one additional term. The executive branch also includes the vice president and the cabinet, which is composed of ministers appointed by the president.
Legislative Branch
Liberia has a bicameral legislature known as the National Legislature, which consists of two chambers:
- Senate: Composed of 30 senators, with each of the 15 counties electing two senators. Senators serve nine-year terms.
- House of Representatives: Composed of 73 representatives, elected based on the population of the constituencies they represent. Representatives serve six-year terms.
Judicial Branch
The judiciary of Liberia is independent and consists of several levels of courts, including:
- Supreme Court: The highest court in the land, headed by the Chief Justice.
- Circuit Courts: Intermediate appellate courts.
- Magisterial Courts: Lower courts that handle minor civil and criminal cases.
Political Parties
Liberia has a multi-party political system. Major political parties include:
- Unity Party (UP)
- Congress for Democratic Change (CDC)
- Liberty Party (LP)
- All Liberian Party (ALP)
Political competition is vigorous, and elections are held regularly to ensure democratic governance.
Recent Political History
Liberia's modern political history has been shaped by civil wars and subsequent peace-building efforts. The two civil wars (1989-1997 and 1999-2003) caused significant disruption and led to international intervention and peacekeeping missions. Since the end of the civil wars, Liberia has made strides toward democratic consolidation and stability.
Elections
Elections in Liberia are held regularly, with presidential, legislative, and local elections occurring at different intervals. The National Elections Commission (NEC) is responsible for overseeing the electoral process, ensuring free and fair elections. International observers often monitor elections to enhance credibility.
Governance Challenges
Liberia faces several governance challenges, including corruption, weak institutions, and limited resources. Efforts are ongoing to improve transparency, accountability, and the rule of law. The government, civil society, and international partners are working together to address these issues.
Foreign Relations
Liberia maintains diplomatic relations with many countries and is a member of various international organizations, including the United Nations (UN), the African Union (AU), and the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS). The country has strong historical ties with the United States, which continue to influence its foreign policy.
Human Rights
Liberia's government is committed to protecting human rights, but challenges remain, particularly regarding gender equality, child rights, and justice for past atrocities. Human rights organizations operate in the country to advocate for and monitor the protection of rights.
Decentralization
There is an ongoing effort to decentralize governance in Liberia to ensure that local governments have more autonomy and resources to address the needs of their communities. This decentralization process aims to improve service delivery and enhance citizen participation in governance.
Liberia's government and political system are centered on democratic principles, with regular elections, multiple political parties, and an independent judiciary. Despite facing significant challenges, Liberia continues to work towards strengthening its institutions and promoting good governance.
COUNTIES OF LIBERIA
Bomi County
Freed slaves and slaves from the Lesser Antilles, who had escaped from their slaveholders or born free left the Caribbean islands and came to Liberia with the help and support from...
Bong County
Named after Mount Bong in the southern portion of the county...
Gbarpolu County
Gbarpolu County has several gold and diamond mines and one of its most popular gold mine company of all time is kongba community gold mines limited popularly know as...
Grand Bassa County
The port of Buchanan was constructed by LAMCO to serve the export of iron ore carried through the railway from Nimba.
Grand Cape Mount County
Portuguese explorer Pedro de Sintra discovered the area of Grand Cape Mount County during 1461. The area was the capital of the Kingdom of Koya.
Grand Gedeh County
Grand Gedeh County is in the eastern portion of the West African nation of Liberia.
Grand Kru County
Kru Coast territory had previously been part of Maryland County, and Sasstown territory had previously been part of Sinoe county.
Lofa County
Lofa County was established from the former Western Province in 1964.
Margibi County
Margibi County was created in 1985 by an Interim National Assembly decree dated December 13, 1985.
Maryland County
Established as a colony of the Maryland State Colonization Society in 1834 but Maryland County was not granted independence until 1854..
Montserrado County
On December 11, 1821 officials from the United States arrived aboard the vessel under the command of Captain Robert F. Stockton at Mesurado Bay.
Nimba County
During the late 1950s, iron ore was found in "the Iron Mountain" Mount Nimba in Nimba County
Rivercess
Eighth largest in area, Rivercess was created in 1984.
River Gee County
River Gee split from River Gee County in May 2000 after receiving approval from Liberia's House of Rep. in May 1997 and Senate approval in March 2000.
Sinoe County
This area became colonized by more than 300 freed African-American slaves from Prospect Hill Plantation, Mississippi in 1845.